
In the realm of modern architecture and interior design, the ground beneath our feet is often overlooked, yet it serves as a crucial foundation for both functionality and aesthetics. Enter the concept of raised floors — an innovative solution that elevates us literally and metaphorically above the traditional concrete slab. As buildings evolve to accommodate advanced technologies, environmental considerations, and the diverse needs of occupants, the merits of installing a raised floor system become increasingly evident. This article delves into the reasons behind opting for a raised floor over concrete, exploring the practical advantages, the enhancement of versatility in design, and the potential for improved building performance. Join us as we uncover how this seemingly simple choice can transform spaces, streamline operations, and pave the way for a more efficient future in architecture.
Table of Contents
- The Benefits of Raised Floors: Elevating Functionality and Aesthetics
- Enhancing Airflow and Temperature Control in Concrete Spaces
- Mitigating Moisture Issues: The Role of Raised Flooring Systems
- Choosing the Right Materials and Installation Techniques for Optimal Performance
- Q&A
- Final Thoughts

The Benefits of Raised Floors: Elevating Functionality and Aesthetics
Opting for a raised floor system over traditional concrete solutions offers a multitude of benefits that enhance both functionality and aesthetics. One of the primary advantages is the flexibility it provides, allowing for easy access to electrical and HVAC systems without compromising the integrity of the floor. This accessibility makes maintenance and upgrades significantly simpler, saving time and reducing costs in the long run. Furthermore, raised floors can facilitate better air circulation, contributing to improved indoor air quality and energy efficiency.
On the aesthetic front, raised floors offer the opportunity for customization that solid slabs simply cannot match. With a variety of materials, colors, and patterns available, these systems can elevate interior design while providing a sleek, modern look. Additionally, the space beneath the raised floor can be utilized for cable management, further decluttering the workspace and contributing to a more organized environment. Here’s a quick comparison of the key benefits:
| Feature | Raised Floors | Concrete Floors |
|---|---|---|
| Accessibility | Easy access to utilities | Difficult to access piping/wiring |
| Customization | Variety of design options | Limited aesthetic choices |
| Airflow | Enhanced ventilation | Restricted airflow |
| Maintenance | Simple to modify | Complex repairs |
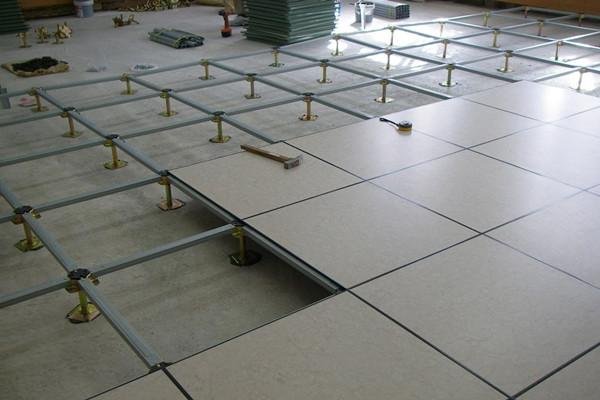

Enhancing Airflow and Temperature Control in Concrete Spaces
Implementing a raised floor system over concrete can significantly enhance airflow and bolster temperature control within a space. This design creates an accessible void under the flooring, allowing for the distribution of air from HVAC systems more efficiently. The improved ventilation can mitigate the accumulation of heat and moisture, particularly in environments where equipment generates substantial thermal loads. Additionally, the raised flooring facilitates the movement of cool air, fostering a more comfortable atmosphere that can be crucial in data centers, offices, and industrial settings. Key benefits include:
- Improved Airflow: Enhances distribution of cool air and reduces hotspots.
- Environmental Control: Allows for better management of humidity and temperature.
- Increased Space Efficiency: Offers easier access for maintenance of electrical and data cabling.
Moreover, the incorporation of a raised floor system can serve as an effective thermal break, aiding in temperature regulation. By elevating the flooring, heat transfer between the concrete and the occupied space is decreased, creating a more stable and controlled climate. This approach not only contributes to comfort but also to energy savings, as HVAC systems can operate more efficiently without the burden of compensating for excessive heat. Here’s a quick comparison of traditional concrete floors versus raised flooring systems in temperature management:
| Feature | Concrete Floor | Raised Floor |
|---|---|---|
| Airflow Distribution | Poor | Excellent |
| Temperature Regulation | Limited | Enhanced |
| Accessibility for Maintenance | Challenging | Easy |
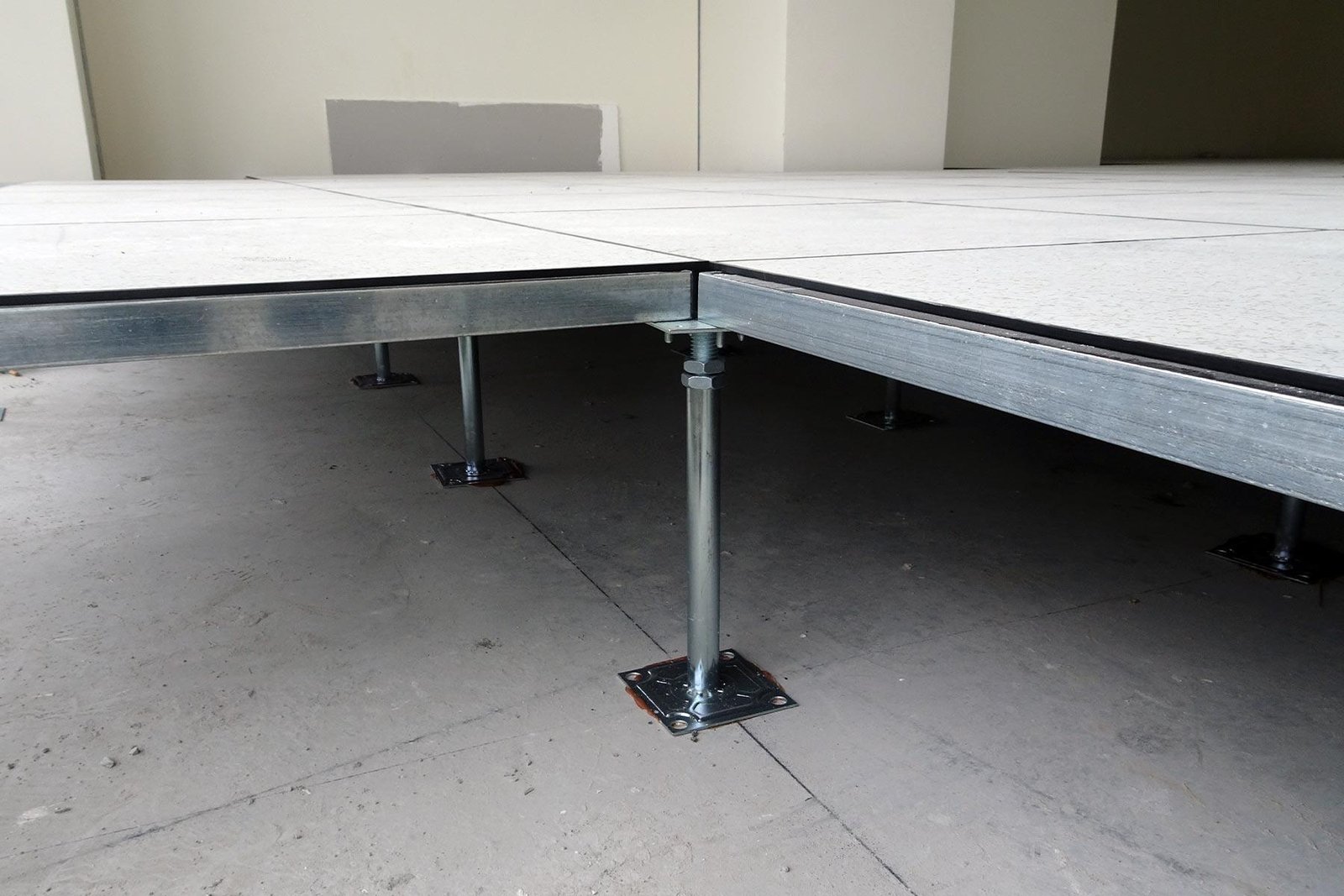

Mitigating Moisture Issues: The Role of Raised Flooring Systems
In environments where moisture control is crucial, elevated flooring systems offer a robust solution. By creating a gap between the concrete slab and the floor surface, these systems effectively reduce the risk of moisture accumulation, promoting a healthier indoor climate. Key benefits include:
- Enhanced Airflow: The space beneath the raised floor allows for improved ventilation, helping to dissipate moisture before it reaches the living area.
- Minimized Water Damage: With elevated flooring, any potential water infiltration can be easily monitored and managed, reducing the likelihood of mold and structural impairment.
- Flexibility in Utilities: The void space can accommodate electrical and plumbing systems, allowing for easy modifications and upgrades without disrupting the entire floor.
Moreover, raised flooring systems are designed with durable materials that withstand fluctuations in humidity. This resilience not only enhances longevity but also protects against the potential for mold growth. When considering moisture-related challenges, it’s essential to understand the properties of these systems:
| Material | Moisture Resistance | Durability |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | High | Very High |
| Vinyl | Moderate | High |
| Laminate | Low to Moderate | Moderate |
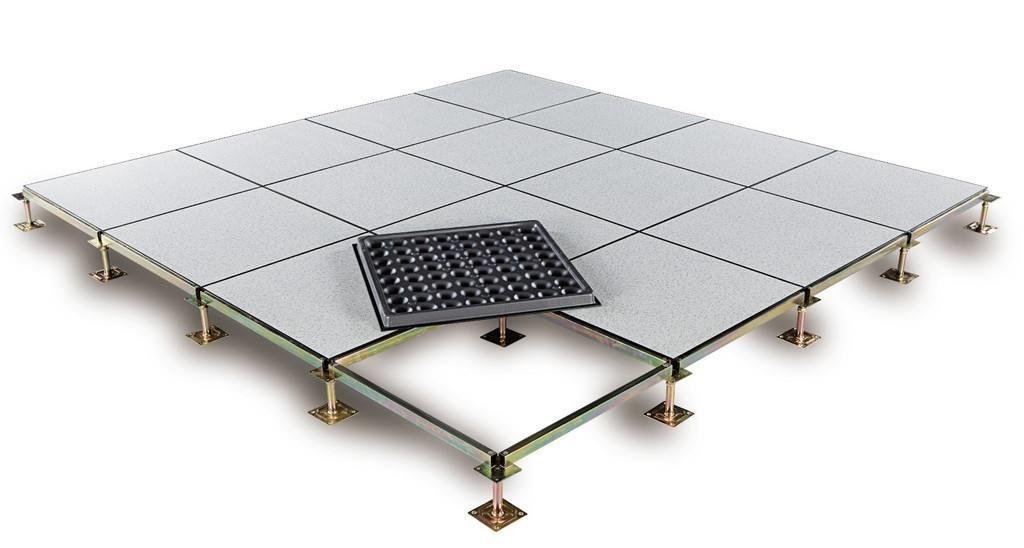
Choosing the Right Materials and Installation Techniques for Optimal Performance
Selecting the best materials for a raised floor system over concrete is crucial to achieve optimal performance and longevity. Materials such as high-density particle board, steel, and aluminum are commonly used for their durability and strength. Each option presents unique advantages; for instance, steel panels can bear heavy loads, making them ideal for data centers, while aluminum offers lightweight properties for applications where mobility is needed. It’s essential to consider the specific requirements of your space—be it load capacity, acoustic performance, or thermal insulation—when choosing your materials.
In addition to materials, the installation techniques play a vital role in the effectiveness of your raised floor system. Proper alignment and secure fastening are fundamental to creating a stable and reliable floor. Here are some recommended techniques:
- Pre-leveling the subfloor to ensure an even base.
- Using adjustable pedestals for flexibility in height.
- Sealing joints to enhance moisture resistance.
Moreover, it’s essential to follow best practices in ventilation planning and cable management to enhance functionality and accessibility. Here’s a simple guide comparing common installation methods:
| Method | Advantages |
|---|---|
| Direct glue-down | Low profile, excellent stability |
| Suspended grid system | Easier access for cable management |
| Panel on pedestal | Height flexibility, quick to install |
Q&A
Q&A: Why Opt for a Raised Floor Over Concrete?
Q1: What exactly is a raised floor system?
A1: A raised floor system is an elevated floor structure that creates a space between the concrete slab foundation and the finished floor. This gap is utilized for the routing of electrical wiring, HVAC systems, and other utilities, making it a popular choice in commercial buildings, data centers, and modern offices.
Q2: Why would someone choose a raised floor over a traditional concrete floor?
A2: There are several compelling reasons! First and foremost, the raised floor allows for greater flexibility regarding reallocating or upgrading utilities. With a traditional concrete floor, modifications can be labor-intensive and disruptive. A raised floor system simplifies future changes, making it easier to adapt to various technological and spatial needs.
Q3: What are the benefits in terms of maintenance?
A3: Maintenance becomes substantially easier with a raised floor. Accessible air and cable routing means that repairs or upgrades can be performed without tearing up the concrete. This can minimize downtime and reduce costs associated with maintenance and renovation work.
Q4: Are there any advantages regarding climate control?
A4: Absolutely! A raised floor system can improve climate control in indoor environments. The space beneath the floor allows for better distribution of air conditioning and heating systems, leading to more efficient temperature management. This can enhance comfort levels, particularly in large, open spaces or data-heavy environments where cooling is critical.
Q5: Can a raised floor contribute to design aesthetics?
A5: Yes, it can! A raised floor system offers opportunities for creative design. The adaptability of materials, finishes, and elevation allows architects and designers to tailor spaces to their aesthetic vision while meeting practical requirements, resulting in both functional and visually appealing environments.
Q6: Is a raised floor system suitable for all spaces?
A6: While raised floors are advantageous in many scenarios, they may not be ideal for all spaces. Lower ceilings or existing structural constraints might hinder installation. Additionally, the initial investment and complexity of installation should be considered, especially for smaller or less tech-centric environments.
Q7: What about cost considerations?
A7: Cost can be a double-edged sword. While the installation of a raised floor system might involve higher upfront costs compared to a traditional concrete slab, these expenses can be offset by long-term savings in maintenance, energy efficiency, and workspace flexibility.
Q8: Can a raised floor system support heavy equipment?
A8: Yes! Modern raised floor systems are designed to support significant loads, making them ideal for data centers and industries where heavy servers and equipment are prevalent. Ensure that the selected system is rated to handle the specific weight and usage requirements of your equipment for optimal performance.
Q9: How can someone determine if a raised floor is the right choice for their project?
A9: Consider assessing the specific needs of your project—think about how you plan to use the space, how often changes might occur, and the critical importance of utilities. Engaging with architects or engineers with experience in raised flooring can provide insights into whether this solution aligns with your vision and functional requirements.
Q10: Any final thoughts?
A10: A raised floor system can be an outstanding investment in adaptability and efficiency, particularly in environments where technology and flexibility reign supreme. As with any architectural decision, carefully weighing the pros and cons in relation to your unique needs will guide you toward the best choice for your space.
Final Thoughts
a raised floor over concrete offers a multitude of benefits that extend far beyond mere aesthetics. It creates a versatile space that accommodates wiring and plumbing needs, promotes better airflow, and enhances the overall functionality of a room. Whether you’re considering this upgrade for a residential setting or a commercial environment, the advantages—such as improved thermal comfort, easier maintenance, and increased adaptability—speak for themselves. By elevating your living or working area, you not only invest in practicality but also create an environment that fosters innovation and creativity. As you weigh the pros and cons, remember that thoughtful decisions today can lay the groundwork for a more efficient, organized, and comfortable tomorrow. Embrace the possibilities a raised floor can unlock—it’s not just a choice; it’s a step toward reimagining your space.

